Using Apache Ranger for Hive Data Access Control
Qubole QDS supports Apache Ranger™ to provide fine-grained data access control in Hive, including row-level filtering and column-level masking. Apache Ranger is a widely-used open source framework that manages and monitors granular data security.
To use Ranger with QDS, you must have Ranger installed in your environment. For information on installing Ranger, see the Apache Ranger web site. Once you have installed Ranger, you will configure it through the Ranger Admin UI, as described in the section below, Configuring Ranger for QDS.
Note
Multiple clusters and multiple services can share a common Ranger Admin.
You also need to install and configure the Ranger plugin for Hive on the QDS clusters to enforce Ranger policies. For details, see the section below, Enforce Data Access Control Policies for Hive.
Supported Versions
The following table shows the currently supported versions of QDS components used with Ranger.
Component |
Supported Versions |
|---|---|
Apache Ranger |
1.1.0 |
HiveServer2 (HS2) |
2.1.1 |
Java |
1.8 |
QDS |
R54 |
Setup
For Ranger authorization to work with Hive, two components are required: Ranger Admin and Ranger Hive Plugin. If LDAP/AD group-based policies are required, a third component, Ranger Usersync, is required, as well. Ranger 1.1.0 requires Java 1.8. Before setup, ensure that Java 8 is installed and its path is exported as JAVA_HOME.
Note
Users can compile and use open source Ranger themselves. For your convenience, we have compiled Ranger and placed the files at s3://paid-qubole/ranger-1.1.0:
s3://paid-qubole/ranger-1.1.0/ranger-1.1.0-admin.tar.gzs3://paid-qubole/ranger-1.1.0/ranger-1.1.0-hive-plugin.tar.gzs3://paid-qubole/ranger-1.1.0/ranger-1.1.0-usersync.tar.gz
Configuring Ranger for QDS
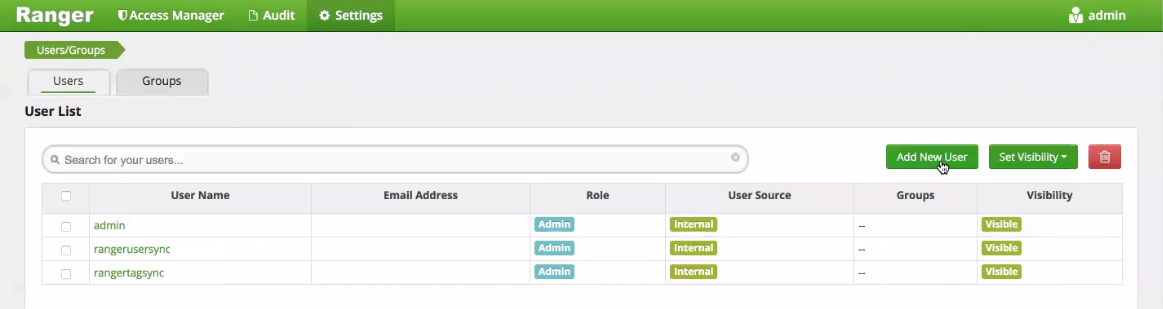
For Hive Server 2 health checks, QDS requires a user with the username qbol_user to be configured on Ranger. Create this user by clicking Add New User in the Users/Groups section of the Ranger Admin UI:
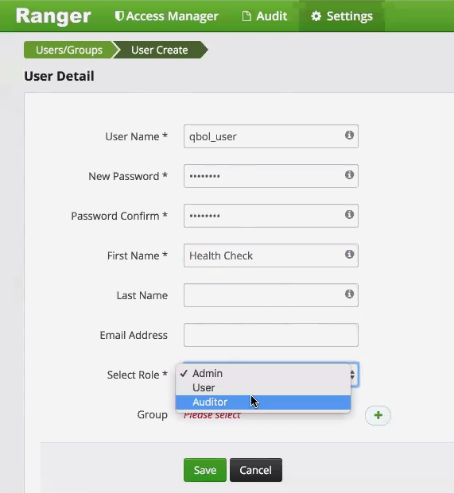
Assign qbol_user the Auditor role:
Give qbol_user read permission on the Hive “default” database by creating a policy in the Create Policy section of the Ranger Admin UI. For database, enter default:
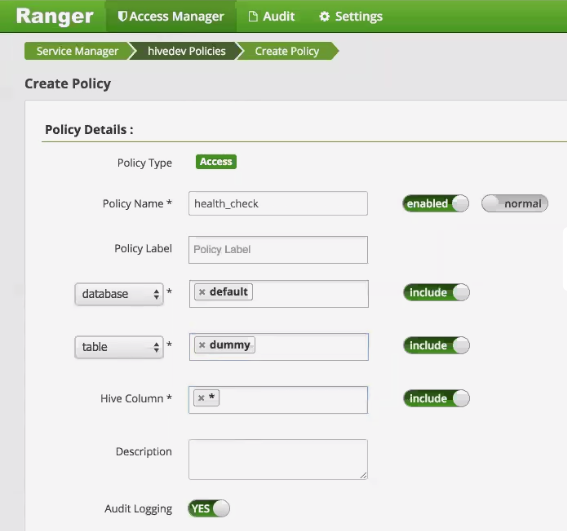
Note
The table for which access is given can be a non-existing dummy table rather than an actual table, as shown above.
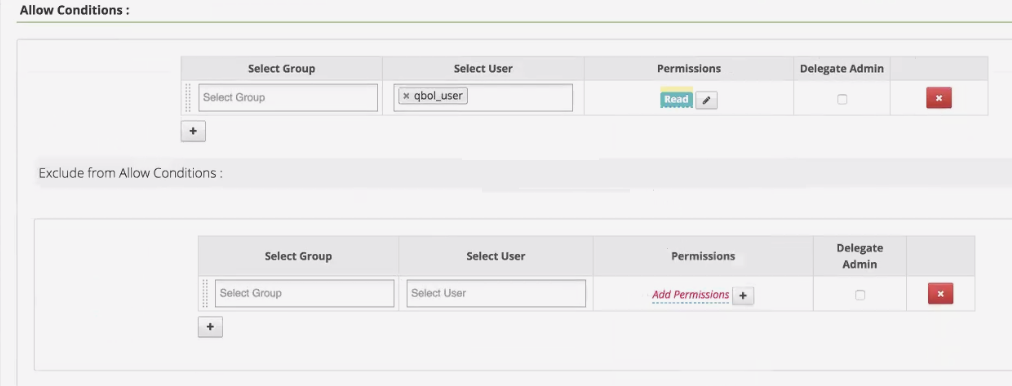
In the Allow Conditions section for the policy, give qbol_user read permissions to the default database.
For any query to run on QDS Hive, the user must have write permission to defloc’s tmp directory in Ranger via a URL-based policy, and the URL should be prefixed and suffixed with wildcard asterisks (*). For example, if defloc were s3://sample-bucket/p1/p2/my_defloc, the URL for which write permission must be granted would be */sample-bucket/p1/p2/my_defloc/tmp/*
Enforce Data Access Control Policies for Hive
Create and configure your Hive service in the Ranger Service Manager by setting any of these policies:
Access: The Access tab lists all the policies you have created for this service, and provides buttons for viewing, editing, or deleting the policies.
Masking: In the Masking tab, you can create column masking policies to hide sensitive data by specifying a database, table, and column, and choosing a type of masking.
Row Level Filter: In the Row Level Filter tab, you can restrict Hive data access to specific rows based on user characteristics, such as group membership.
Note
A JDBC URL is not required, and you can specify “None” for the required configuration properties.
Bootstrapping a Cluster with Ranger
Qubole provides a bootstrap script that configures your clusters to use Ranger. Contact Qubole Support to obtain the bootstrap script. This script includes URLs and other parameters for which you must provide values appropriate to your own environment. For details on these parameters, see the commented-out lines within the bootstrap script itself.
Note
Wait for the node bootstrap process to complete before using the cluster. The bootstrap process normally completes within a couple of minutes.
Using LDAP or Active Directory
When configuring Ranger with LDAP or Active Directory, use Hadoop Overrides in the cluster configuration page to override the Hadoop properties required for Group mapping. For more information, see LDAP Groups Mapping on the Hadoop Groups Mapping page on the Apache Hadoop web site. Consult with your LDAP or Active Director provider for any additional required properties.
Additional Considerations when Using Ranger
The Ranger authorization plugin does not support role-based statements (such as
CREATE ROLE role_nameorSHOW CURRENT ROLES), and will throw an exception if these are used.To grant or revoke privileges for another user with
GRANTorREVOKESQL statements on the Qubole UI, the current user must have the roledelegateAdmin. This role is configured with a check box when creating the policy, or with a SQL statement like the following:grant select ON TABLE <table> to USER <user> with grant optionIn a non-LDAP setup, QDS cannot determine the user’s group, so Ranger policies that are targeted for groups won’t work in a non-LDAP setup.
Masking and row-filtering policies in Ranger cannot contain wildcards; each column must have a policy for itself.
On clusters configured with Ranger policies, Ranger policies will take priority over Hive Authorization, because it is set up using bootstrap.
Test Connection while creating a new Hive service on Ranger is not supported.
QDS does not support Ranger autocomplete.