Using Heterogeneous Nodes in Hadoop 2/Presto/Spark Clusters
For a heterogeneous cluster:
The QDS UI displays supported instance types with weights based on instance memory. You can use the scrollable counter to change the weight as needed.
The first instance type must be the same as the cluster’s worker instance type and have a weight of 1.0. This is the primary instance type. Make sure that the first instance type is the primary instance type if you are using Qubole’s APIs to create a heterogeneous cluster.
QDS will try the rest of the instance types whenever it needs to provision nodes and when nodes from the earlier list are unavailable. The number of instances requested is decided by the weight.
For example, during autoscaling on AWS, QDS may decide that it needs 10 m4.4xlarge nodes. But if this instance type is unavailable, QDS tries to get 20 m4.2xlarge nodes instead. On AWS, this is only true for On-Demand nodes. However, with Spot instances, Qubole uses AWS spot fleet, so QDS will obtain the cheapest combination of nodes of different types that satisfies the target capacity.
For more information on the API configuration option, heterogeneous_instance_config, see Create a New Cluster,
Clone a Cluster or Edit a Cluster Configuration.
Selecting different instance types using the QDS UI
See Configuring Heterogeneous Worker Nodes in the QDS UI for information about configuring heterogeneous nodes.
The sections that follow provide two examples using AWS.
Choosing Heterogeneous Worker Nodes from the Same Instance Family (AWS Example)
Let us consider configuring heterogeneous nodes of the AWS c3 instance family in a new Hadoop 2 cluster.
Note
In case of Presto clusters, you must carefully pick instance types, which have similar CPU and memory capacity.
Choosing instances types with significantly different CPU and memory capacity may lead to degraded performance
and increased query failures as the weakest configuration instance would be the bottleneck during query execution.
Qubole recommends you to first pick an instance family type (r/m/c) and then choose instance types
of the same size, which are not more than one generation apart. For example, (r3.2xlarge, r4.2xlarge),
(r4.4xlarge, r5.4xlarge, r5a.4xlarge), (c4.8xlarge, c5.8xlarge) and so on.
Perform the following steps to select multiple instance types:
Navigate to the Clusters page. Click New to add a new cluster.
Select Hadoop 2 as the cluster type.
Go to the Configuration tab. Specify at least one cluster label.
Select the c3.large as the Coordinator node type from the c3 family.
Select the c3.xlarge first worker node type from the c3 family. The first worker node type is the primary worker instance type.
Since Qubole supports heterogeneity in On-Demand and Spot instances, decide on the cluster composition based on the nodes that you have purchased.
Enable Use Multiple Worker Node Types to configure other worker instance types of the c3 instance family.
Select c3.8xlarge as one worker node type.
Qubole displays the weight of that worker node type. Override the default weight if you want to base it on the number of CPUs, cost, or any other parameter. The default node weight is calculated as (memory of the node type ÷ memory of the primary worker type).
Click Add worker node type to add another worker node type.
Select c3.2xlarge as another worker node type.
Qubole allows you to add a maximum of 10 worker node types.
The minimum number of nodes is by default 1. The maximum number of nodes in the cluster configured can be satisfied either by provisioning the corresponding number of nodes of the primary worker type or a combination (based on weights) of nodes across all configured instance types. For example, if the maximum is configured as 100, then this can be fulfilled either by 100 c3.xlarge nodes or 50 c3.2xlarge nodes, or 12 c3.8xlarge or a combination thereof such as 50 c3.xlarge and 6 c3.8xlarge nodes.
Note
Depending on the mix of instance types and weights you configure, upscaling can cause the actual number of nodes running in the cluster to exceed the configured Maximum Worker Nodes. See Why is my cluster scaling beyond the configured maximum number of nodes?
The following figure illustrates the heterogeneous worker nodes that are described in the above steps.
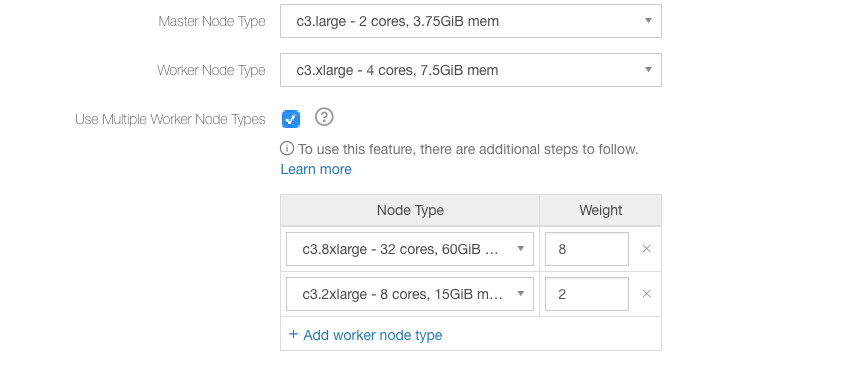
In the above figure, c3.xlarge is the first worker instance type and its weight is 1.0.
Refer to Managing Clusters for information on the rest of the cluster configuration.
Note
The NodeManager properties, yarn.nodemanager.resource.memory-mb and yarn.nodemanager.resource.cpu-vcores
must not be overridden in heterogeneous clusters as it hampers the normal operations and performance of the
cluster.
Choosing Heterogeneous Worker Nodes from Different Instance Families (AWS Example)
Let us consider configuring heterogeneous nodes with AWS c3, c4, and r3 worker node instance types in a new Hadoop 2 cluster.
Note
In case of Presto clusters, you must carefully pick instance types, which have similar CPU and memory capacity.
Choosing instances types with significantly different CPU and memory capacity may lead to degraded performance
and increased query failures as the weakest configuration instance would be the bottleneck during query execution.
Qubole recommends you to first pick an instance family type (r/m/c) and then choose instance types
of the same size, which are not more than one generation apart. For example, (r3.2xlarge, r4.2xlarge),
(r4.4xlarge, r5.4xlarge, r5a.4xlarge), (c4.8xlarge, c5.8xlarge) and so on.
Perform the following steps to select multiple instance types:
Navigate to the Clusters page. Click New to add a new cluster.
Select Hadoop 2 as the cluster type.
Go to the Configuration tab. Specify at least one cluster label.
Select the c3.large as the Coordinator node instance type from the c3 family.
Select the c3.xlarge worker node first instance type from the c3 family. The first worker instance type is the primary worker instance type.
Since Qubole supports heterogeneity in On-Demand and Spot instances, decide on the cluster composition based on the nodes that you have purchased.
Enable Use multiple save node types to configure other worker instance types of the c4 and r3 instance families.
Select c4.2xlarge as one worker node type.
Qubole displays the weight of that worker node type. Override the default weight if you want to specify it based on the number of CPUs, cost, or any other parameter. The default node weight is calculated as (memory of the node type ÷ memory of the primary worker type).
Click Add worker node type to add another worker node type.
Select r3.2xlarge as another worker node type.
Qubole allows you to add a maximum of 10 worker node types.
The maximum number of nodes in the cluster configured can be satisfied either by provisioning the corresponding number of nodes of the primary worker type or a combination (based on weights) of nodes across all configured instance types. For example, if the maximum is configured as 100, then this can be fulfilled either by 100 c3.xlarge nodes or 50 c3.2xlarge nodes, or 12 r3.2xlarge or a combination thereof such as 50 c3.xlarge and 6 r3.2xlarge nodes.
The following figure illustrates the heterogeneous worker nodes that are described in the above steps.
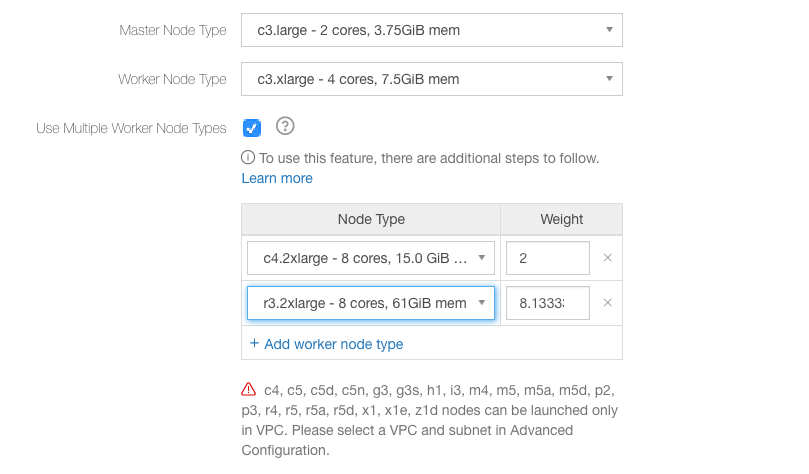
In the above figure, c3.xlarge is the first worker instance type and its weight is 1.0.
Refer to Managing Clusters for information on the rest of the cluster configuration.