GitLab Version Control for Zeppelin Notebooks
To configure the version control for Notebooks using GitLab, you must perform the following tasks:
After configuring the GitLab Repository, you can perform the following tasks to manage the notebook versions:
Configuring a GitLab Token
You can configure a GitLab Token for notebooks at per user setting level from the My Accounts or Notebooks UI.
To configure the GitLab token for notebooks at your account level, see Configuring a GitLab Token.
To configure the GitLab token from notebooks, perform the following steps:
Navigate to Notebooks and click a notebook.
Click Manage notebook versions that is on the top-right of the notebook. The Versions panel expands as shown in the following figure.
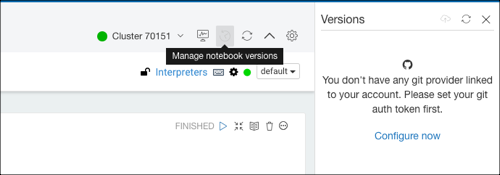
Click Configure now.
In the dialog box add the generated GitLab token and click Save.
The GitLab token is now configured for your account.
Linking Notebooks to GitLab
After configuring the GitLab token, you can link the GitLab repository from notebooks.
Navigate to the GitLab profile and copy the URL from the browser’s address-bar.
Note
If you want to add
HTTPS *.gitlink as the GitLab repository URL, click Clone or Download. A drop-down text box is displayed. Copy the HTTPS URL or click Use HTTP (if it exists) to copy the HTTPS URL.Click Manage notebook versions icon that is on the top-right of the notebook. The Versions panel expands as shown in the following figure.
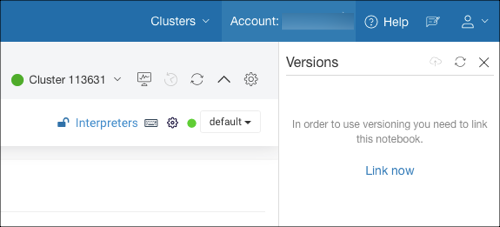
Click the Link Now option.
In the Link Notebook to GitLab dialog box, perform the following actions:
Add the GitLab repository URL in the Repository Web URL text field. Ensure that the GitLab profile token has read permissions for the repository to checkout a commit and write permissions for the repository to push a commit.
Select a branch from the Branch drop-down list.
Add an object path file in the Object Path text field.
A sample is as shown in the following figure.
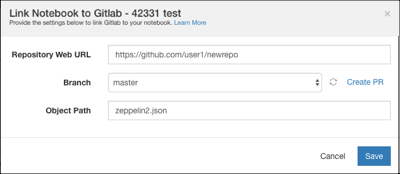
Click Save.
Pushing Commits to GitLab
After you link notebooks with a GitLab repository, you can start using the notebook to push commits to the GitLab directly from a notebook associated with a running cluster.
Before you push the commits, ensure that the following requirements are met:
The GitLab profile token must have write permissions for the repository to push commits.
The associated cluster must be running.
Steps
Click Manage notebook versions that is on the top-right of the notebook. It expands and provides the version details.
Click the Push icon to commit. A dialog opens to push commits. The following figure shows the version details and the Push to GitLab dialog.
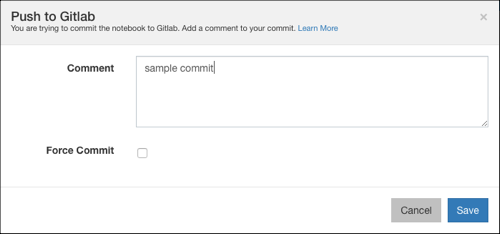
Add a commit message and click Save to push the commit to the GitLab repository. You can use the option force commit to force push over the old commit (irrespective of any conflict).
Note
Qubole does not store commits or revisions of notebooks. However, commits or revisions of notebooks can be fetched from users’ GitLab account whenever required.
Restoring a Commit from GitLab
Click Manage notebook versions that is on the top-right of the notebook. It expands and provides the version details.
Select a version from the list and click Restore to checkout that version as shown the following figure.
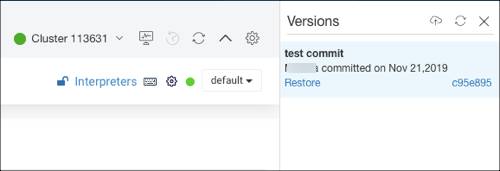
Click OK to checkout that version in the confirmation dialog box.
Note
Qubole does not store commits or revisions of notebooks. However, commits or revisions of notebooks can be fetched from users’ GitLab account whenever required.
Creating a Pull Request from Notebooks
Open the required notebook.
Click on the Gear icon on the top right corner of the notebook, and select Configure GitLab Link. The Link Notebook to GitLab dialog is displayed.
Click on the Create PR hyperlink.
Proceed with the steps in GitLab to create the PR.
For more information, see GitLab Documentation.
Resolving Conflicts While Using GitLab
There may be conflicts while pushing/checking out commits in the GitLab versions.
Note
You can use the option force commit to force push over the old commit (irrespective of any conflict).
Perform the following steps to resolve conflicts in commits:
Clone the notebook.
Link the cloned notebook to the same GitLab repo branch and path as the original notebook.
Checkout the latest version of the cloned notebook.
Manually port changes from the original notebook to the cloned notebook.
You can commit the cloned notebook after porting changes.